Ammar Badwy | Posted on August 28, 2021
This is how new APIs are discovered
You probably know, in general, what the process of a new medicine looks like. But what about the active substance of the medicines? How are they discovered? Is it by accident similar to how Penicillin is discovered? Or is it the other way around? You’ll find out in this blog. And we’ll tell you what the journey of a new API looks like.
In the olden days, active ingredients for medicine were usually extracted from plants or animals. For example, Quinine, a well-known drug for treating Malaria, was first isolated from the Cinchona tree’s bark, typically found in Peru.
Even though some specific ingredients are still sourced from a biological source, new pharmaceuticals are rarely sourced anymore through these methods. Simply because, due to centuries’ worth of history, they have all been invented already. But also because modern technology can be more efficient, safer, and cleaner.
Drug discovery
Historically, when a new drug was discovered, it wasn’t known how it would interact with the body and its purpose as medication; this was only found after discovering the drug. This is known as “Classical Pharmacology.”
With scientific advances and our current knowledge, however, it has become more typical to perform this reverse process called “Target-based drug discovery.” A specific target in the body is chosen, and then it is screened which group of molecules works best for that part of the body, further narrowed down to one or two specific compounds.
Science
Chemical synthesis is what shaped the pharmaceutical industry as we know it. Scientists in laboratories can create new APIs by having two or more materials react with each other, and this isn’t limited to just one reaction; there can be dozens of steps from start to finish.
An example of a chemical reaction that you might know is how concrete is formed. When you mix cement powder with water and a few other ingredients, a chemical process takes place, and turns into concrete with different chemical properties. And this isn’t reversible; if you were to grind up the concrete, you can’t simply add water again to use it as cement; it has already become something else. Chemical reactions like this happen all the time during the production process of an API.
Returning to the lab with promising new stable substances, scientists perform further research and development. Pharmacological research is performed to know exactly how and if a new API works as a medicine.
Traditionally, a lot of this research was performed on animals, but thanks to technological progression and our scientific knowledge, a large portion of the testing can also be done on cell cultures in Petri dishes. However, animal research is still necessary and sometimes even mandatory to understand how the new medicine works on an entire organism.
Regarding vaccines and antibiotics, the pharmaceutical industry mostly utilizes biotechnology instead of chemical synthesis. In short, it is about using microorganisms such as bacterias to help the body to fight diseases.
Typically your body would have substances to fight diseases by nature. But if they are missing or aren’t sufficiently present enough in the body, we have modified microorganisms that can create those substances in the body by using clever technology. So it would be able to fight disease by itself.
Scaling up
So going back to APIs and that process again, after all the development on a lab scale, research on animals, trials, and everything in between, it’s time to scale up. Having to produce a pharmaceutical raw material on a huge industrial scale isn’t the same as making a small batch in a lab.
Most likely, the producers will encounter problems on the large-scale production sites that they didn’t have during the small lab scale, for example, how the large equipment handles the mixing of the components or if the drying process can be performed as quickly as is necessary.
From API to medicine
And then there’s still the question of how the API should be administered to people to work at its best. And for the patient to conveniently use the medicine themselves? Tablets, injections, capsules, ointment?
The most efficient method is chosen based on things like the particle size of the API, solubility, and researching how long the API stays active in each form.
So that’s it! It starts with chemical synthesis or biotechnology, followed by a decade or longer of research and development, and then actual production on a large scale.
Of course, this is just scratching the surface of how APIs and medicine are produced, but I hope it gives you an idea about the process and the history of pharma.
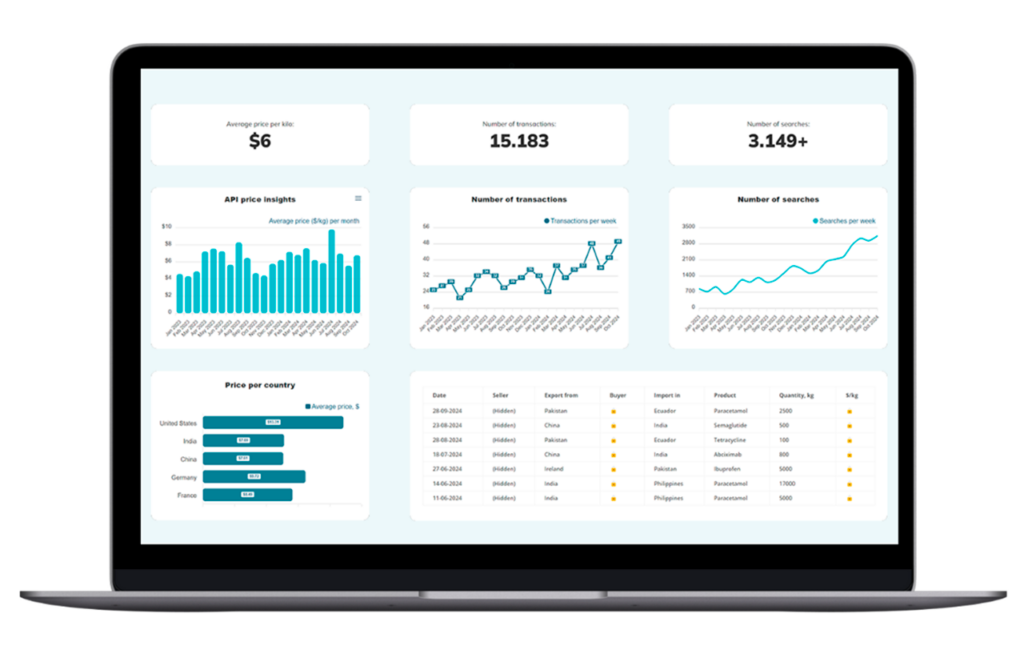
Want to be sure you’re paying a fair price for your APIs? Now it’s easy.
Pharmaoffer’s Trade Data service gives you an overview of the latest average selling prices, transaction volumes, and tracking search data across the globe for thousands of APIs.
Simplify your sourcing process by accessing current market insights and detailed transaction histories that will give your business a competitive edge.
Check it out today and make smarter sourcing decisions!
FAQ
I have written this blog to the best of my knowledge and belief. I’m not a pharmacist and don’t bear the responsibility for any errors or mistakes.